



Next: Flagging (UV_FLAG, RUN UV_MFLAG,
Up: Interacting with tables
Previous: Advanced
Contents
Index
Visualization (GO UVALL and GO UVCOV)
Although images are a wonderful way to display results, problems may be
more obvious in scatter plots of visibilities. For instance, large strips
in the dirty image often originates from a single outlier visibility.
GO UVALL is a procedure to explore the content of a 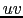 table
through visualization of scatter plots. This procedure is controlled by
several input parameters, in particular the following global variables
table
through visualization of scatter plots. This procedure is controlled by
several input parameters, in particular the following global variables
- NAME
- The filename without extension of the input
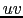 table;
table;
- XTYPE and YTYPE
- The types of data to be plotted
along the X and Y axes. These two variables can take the following values
- u or v
- Fourier coordinates [m];
- radius
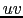 distance (
distance (
 ) [m];
) [m];
- angle
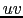 position angle (atan2(V,U)) [deg];
position angle (atan2(V,U)) [deg];
- time
- UT time of observation [hrs];
- date
- Date of observation [days];
- scan
- Scan number;
- number
- Visibility number in
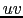 table;
table;
- amp
- Amplitude of visibility [Jy];
- phase
- Phase of visibility [deg];
- real
- Real part of visibility [Jy];
- image
- Imaginary part of visibility [Jy];
- weight
- Weights of visibility [*** ? JP ***].
The default is to plot the amplitude vs the radius of the visibilities.
- FIRST and LAST,
- i.e. the first and last channel to
plot. By default, all channels are plotted.
Other input parameters are available. Please type input uvall to
obtain the most recent available help. For instance, to obtain the scatter
plots of amplitude vs weight of the visibility (which should look like an
hyperbole), you would type:
1 let name 12cs21
2 let xtype weight
3 let ytype radius
4 go uvall
The plot of the 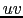 coverage of the data is such an important subset of
the GO UVALL possibility that we created a dedicated procedure for
it, namely GO UVCOV.
coverage of the data is such an important subset of
the GO UVALL possibility that we created a dedicated procedure for
it, namely GO UVCOV.




Next: Flagging (UV_FLAG, RUN UV_MFLAG,
Up: Interacting with tables
Previous: Advanced
Contents
Index
Gildas manager
2014-07-01
![]() table
through visualization of scatter plots. This procedure is controlled by
several input parameters, in particular the following global variables
table
through visualization of scatter plots. This procedure is controlled by
several input parameters, in particular the following global variables