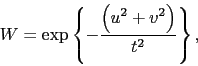



Next: Implementation (READ UV, UV_MAP
Up: Image size, pixel size,
Previous: Link between pixel size
Contents
Index
The use of the visibility weights 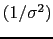 in the definition of the
sampling function is called natural weighting as it is natural to weight
each visibility by the inverse of noise variance. Natural weighting is also
the way to maximize the point source sensitivity in the final image.
However, the exact scaling of the sampling function is an additional degree
of freedom of the imaging process. In particular, the user may change this
scaling to give more or less weight to the large/short spatial frequencies.
in the definition of the
sampling function is called natural weighting as it is natural to weight
each visibility by the inverse of noise variance. Natural weighting is also
the way to maximize the point source sensitivity in the final image.
However, the exact scaling of the sampling function is an additional degree
of freedom of the imaging process. In particular, the user may change this
scaling to give more or less weight to the large/short spatial frequencies.
We can thus introduce a weighting function 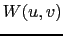 in the definitions of
in the definitions of
 and
and

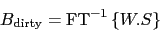 |
(4.4) |
and
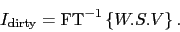 |
(4.5) |
There are two main categories of weighting functions
- Robust weighting
- In this case,
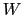 is computed to enhance the
contribution of the large spatial frequencies. This is done by first
computing the natural weight in each cell of the
is computed to enhance the
contribution of the large spatial frequencies. This is done by first
computing the natural weight in each cell of the 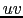 plane. Then
plane. Then 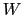 is
derived so that
is
derived so that
- The product
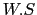 in a
in a 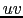 cell is set to a constant if the
natural weight is larger that a given threshold;
cell is set to a constant if the
natural weight is larger that a given threshold;
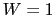 (i.e. natural weighting) otherwise.
(i.e. natural weighting) otherwise.
This decreases the weight of the well measured 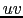 cells (i.e. very
low noise cells) while it keeps natural weighting of the noisy cells. It
happens that the cells of the outer
cells (i.e. very
low noise cells) while it keeps natural weighting of the noisy cells. It
happens that the cells of the outer 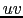 plane (corresponding to the
large interferometer configurations) are often noisier that the cells of
the inner
plane (corresponding to the
large interferometer configurations) are often noisier that the cells of
the inner 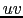 plane (just because there are less cells in the inner
plane (just because there are less cells in the inner
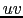 plane). Robust weighting thus increase the spatial resolution by
emphasizing the large spatial frequencies at the cost of a worst
sensitivity to point sources...
plane). Robust weighting thus increase the spatial resolution by
emphasizing the large spatial frequencies at the cost of a worst
sensitivity to point sources...
- Tapering
- is the apodization of the
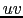 coverage by simple
multiplication of a Gaussian
coverage by simple
multiplication of a Gaussian
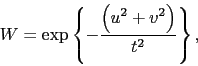 |
(4.6) |
where 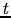 is the tapering distance. This multiplication in the
is the tapering distance. This multiplication in the 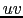 plane translates into a convolution by a Gaussian in the image plane,
i.e. a smoothing of the result. The only purpose of this is to increase
the sensitivity to extended structure. Tapering should almost never be
used as this somehow implies that you throw away large spatial
frequencies measured by the interferometer... In other words, use compact
configuration of the arrays and not tapering to increase sensitivity to
extended structures in your source.
plane translates into a convolution by a Gaussian in the image plane,
i.e. a smoothing of the result. The only purpose of this is to increase
the sensitivity to extended structure. Tapering should almost never be
used as this somehow implies that you throw away large spatial
frequencies measured by the interferometer... In other words, use compact
configuration of the arrays and not tapering to increase sensitivity to
extended structures in your source.
For more details on the whole imaging process the interested reader is
referred to Guilloteau (2000).




Next: Implementation (READ UV, UV_MAP
Up: Image size, pixel size,
Previous: Link between pixel size
Contents
Index
Gildas manager
2014-07-01
![]() in the definition of the
sampling function is called natural weighting as it is natural to weight
each visibility by the inverse of noise variance. Natural weighting is also
the way to maximize the point source sensitivity in the final image.
However, the exact scaling of the sampling function is an additional degree
of freedom of the imaging process. In particular, the user may change this
scaling to give more or less weight to the large/short spatial frequencies.
in the definition of the
sampling function is called natural weighting as it is natural to weight
each visibility by the inverse of noise variance. Natural weighting is also
the way to maximize the point source sensitivity in the final image.
However, the exact scaling of the sampling function is an additional degree
of freedom of the imaging process. In particular, the user may change this
scaling to give more or less weight to the large/short spatial frequencies.
![]() in the definitions of
in the definitions of
![]() and
and
![]()