



Next: Formation of the CLEAN
Up: The family of CLEAN
Previous: CLEAN ideas
Contents
Index
Several criteria may be used to stop the iterative search of this
``matching pursuit'':
- The total number of clean components. This is a sanity criterion in
case the two other ones would be badly tuned.
- When the maximum of the absolute value of the residual map is lower
than a fraction of the noise. This stopping criterion is adapted to
noise limited situations, i.e. when empirical measures of the
noise in the cleaned image give a value similar to the noise value
estimated from the system temperatures.
- When the maximum of the absolute value of the residual map is lower
than a fraction of the maximum intensity of the original dirty map. This
stopping criterion is adapted to dynamic limited situations, i.e.
when some part of the source is so intense that the associated side lobes
are larger than the thermal noise. In this case, any empirical measure of
the noise in the cleaned image will give a value larger than the noise
value estimated from the system temperatures.
Choosing the good stopping criterion is important because the deconvolution
must go deep enough to be correct but CLEAN algorithms start to diverge
when the noise is cleaned too deep. A good compromise is to clean up to or
slightly below (typically 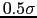 ) the noise level.
) the noise level.




Next: Formation of the CLEAN
Up: The family of CLEAN
Previous: CLEAN ideas
Contents
Index
Gildas manager
2014-07-01